The best treatment for spinal cord injury is surgery, which often involves removing fragments of bones, foreign objects, herniated disks, or fractured vertebrae that are compressing the spine. Surgery may also be necessary to stabilize the spine and prevent future pain or deformity.
Currently, there is no way to reverse the damage to the spinal cord, so treatment focuses on preventing further injuries. This can include physical therapy, the use of assistive devices like wheelchairs or walkers, and occupational therapy. Medications may also be given to manage symptoms.
Seeking immediate treatment can help reduce long-term effects and improve outcomes for individuals with spinal cord injury.
Understanding Spinal Cord Injury
Surgery is often necessary to treat spinal cord injuries, removing any fragments of bones or herniated disks that may be compressing the spine. Stabilizing the spine through surgery can prevent future pain and deformity. While there is currently no way to reverse spinal cord damage, treatment focuses on preventing further injuries and managing symptoms through physical therapy and adaptive devices.
Anatomy Of The Spinal Cord:
- The spinal cord is a long, cylindrical bundle of nerves that extends from the base of the brain down to the lower back.
- It is protected by the vertebrae of the spine, which act as a bony shield.
- The spinal cord is responsible for transmitting messages between the brain and the rest of the body, allowing for movement, sensation, and control of bodily functions.
- It is made up of millions of nerve fibers, divided into different regions called segments.
- Each segment of the spinal cord corresponds to a specific area of the body and controls the functions of that area.
Causes Of Spinal Cord Injury:
- Spinal cord injury can be caused by various factors, including:
- Traumatic incidents such as car accidents, falls, or sports-related injuries.
- Non-traumatic causes, like tumors, infections, or degenerative diseases.
- Damage to the spinal cord can result from a fracture, dislocation, or compression of the vertebrae, leading to a loss of function below the level of the injury.
- The severity of the injury can vary, with some individuals experiencing partial mobility and sensation, while others may be completely paralyzed.
Classification Of Spinal Cord Injury:
- Spinal cord injuries are classified based on the severity and location of the damage.
- The two main types of spinal cord injury classifications are complete and incomplete.
- A complete spinal cord injury refers to a total loss of motor and sensory function below the level of the injury. This often leads to paralysis.
- An incomplete spinal cord injury means that some motor or sensory function is retained below the level of the injury.
- Incomplete injuries can be further categorized based on the affected areas of the body, such as quadriplegia (involving all four limbs) or paraplegia (involving the lower body).
- The classification of spinal cord injury is crucial in determining the appropriate treatment and prognosis for individuals with such injuries.
Medical Interventions For Spinal Cord Injury
Surgery is often necessary to treat spinal cord injury, removing fragments of bones, herniated disks, or fractured vertebrae that compress the spine. Additionally, surgery may be needed for stabilization to prevent future pain or deformity. There is currently no way to reverse spinal cord damage, so treatment focuses on preventing further injuries and managing symptoms through physical therapy and medications.
Surgery For Spinal Cord Injury:
- Surgery is a common medical intervention for spinal cord injury, especially in cases where there is compression or damage to the spine.
- The purpose of surgery is to remove fragments of bones, foreign objects, herniated disks, or fractured vertebrae that may be compressing the spinal cord.
- Surgery may also be necessary to stabilize the spine and prevent future pain or deformity.
- It is important to note that surgery cannot reverse the damages to the spinal cord, but it can help alleviate some symptoms and prevent further complications.
The Role Of Medication In Spinal Cord Injury Treatment:
- Medication plays a crucial role in the treatment of spinal cord injury by managing symptoms and promoting healing.
- Pain medications, such as opioids or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can help alleviate chronic pain associated with spinal cord injury.
- Muscle relaxants may be prescribed to reduce muscle spasms and improve mobility.
- Corticosteroids, such as methylprednisolone, may be administered shortly after injury to reduce inflammation and prevent further damage.
- Other medications, such as antispasmodics or anticonvulsants, may be prescribed to manage specific symptoms like muscle spasms or seizures.
Innovative Treatments And Therapies:
- In recent years, there have been advancements in innovative treatments and therapies for spinal cord injury.
- Stem cell therapy shows promising results in promoting nerve regeneration and restoring function in individuals with spinal cord injury.
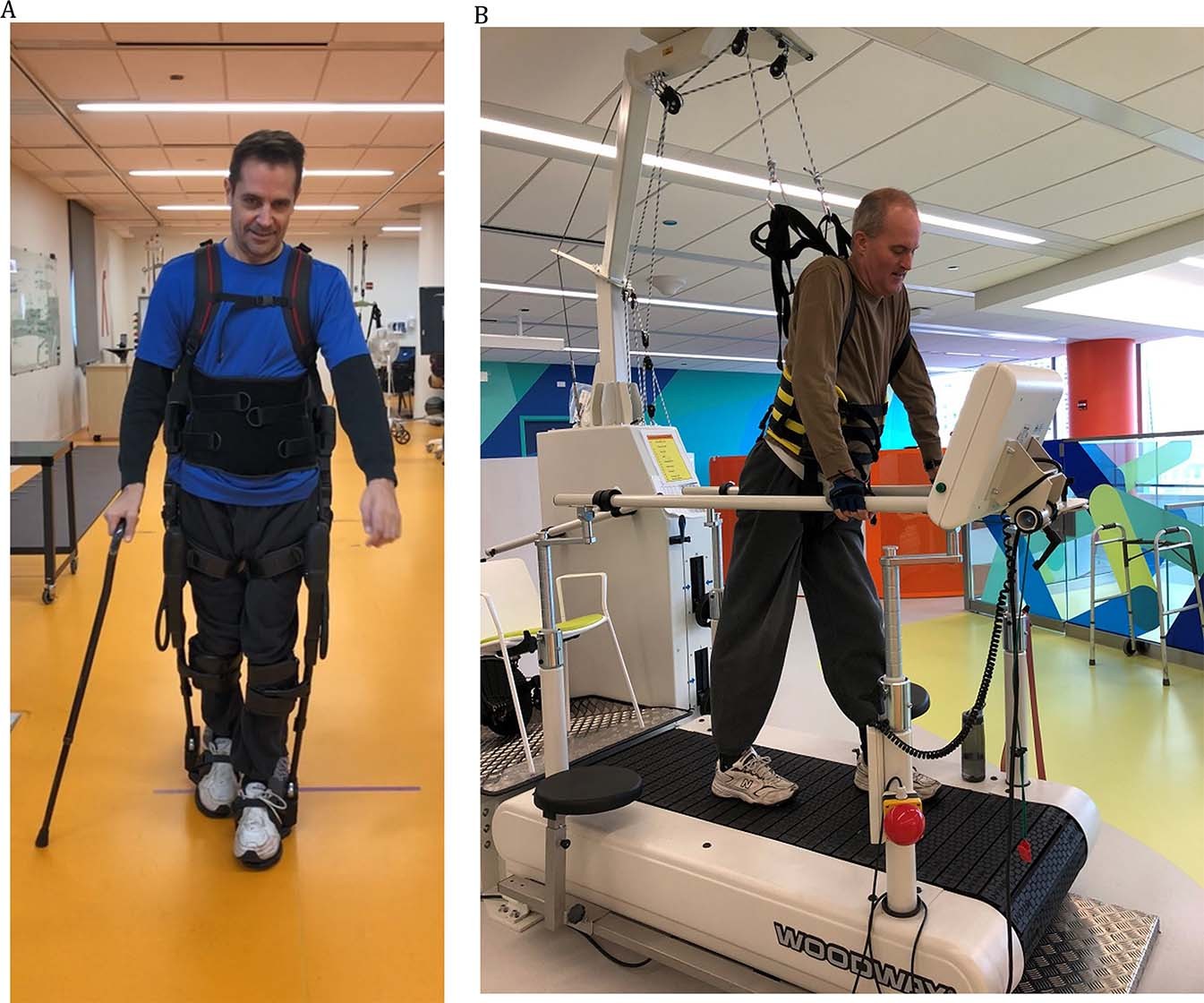
- Robotic exoskeletons and electric stimulation devices help individuals regain mobility and improve their quality of life.
- Virtual reality and augmented reality technologies are being used for rehabilitation purposes, providing immersive and interactive therapy sessions.
- Neurorehabilitation programs focus on intensive physical therapy and occupational therapy to improve motor function and independence.
Remember, treatment for spinal cord injury is multidisciplinary, and the specific interventions and therapies used may vary depending on the individual’s condition, severity of the injury, and response to treatment. It is essential for individuals with spinal cord injury to work closely with their healthcare team to develop a personalized treatment plan.
Rehabilitation And Recovery Strategies
Discover effective rehabilitation and recovery strategies to treat spinal cord injuries. From surgery to remove fragments and stabilize the spine to physical therapy and assistive devices, these treatments aim to prevent further damage and improve mobility and quality of life.
Physical therapy for spinal cord injury patients:
- Physical therapy plays a crucial role in helping spinal cord injury patients regain strength, mobility, and independence.
- It focuses on muscle strengthening, coordination, and mobility to improve overall physical function.
- It may include exercises, stretches, and range of motion activities tailored to the individual’s specific needs and abilities.
- Physical therapists use various techniques and equipment, such as electrical stimulation and body-weight support systems, to facilitate rehabilitation.
- The goal of physical therapy is to maximize function and enhance the patient’s quality of life.
Assistive devices and technology for spinal cord injury patients:
- Assistive devices and technology can greatly improve the independence and quality of life for individuals with spinal cord injuries.
- Wheelchairs, both manual and motorized, provide mobility and allow patients to navigate their surroundings.
- Adaptive equipment, such as grab bars, ramps, and modified utensils, can assist with daily activities and tasks.
- Advanced technologies, like robotic exoskeletons and functional electrical stimulation, can help regain movement and functionality.
- Communication devices, such as voice recognition software and electronic communication aids, enable individuals with limited mobility to express themselves effectively.
Psychological support and counseling for spinal cord injury patients:
- Spinal cord injuries can have a significant emotional impact on patients and their loved ones, requiring psychological support and counseling.
- Counseling can help individuals cope with the emotional challenges and changes in their lives, such as grief, anxiety, and depression.
- Support groups provide an opportunity for individuals to connect with others facing similar challenges, share experiences, and gain support.
- Mental health professionals can assist in developing coping strategies, improving self-esteem, and promoting psychological well-being.
- Family counseling may also be beneficial in helping loved ones understand and adjust to the changes brought about by the injury.
Rehabilitation and recovery strategies for spinal cord injury patients involve physical therapy to enhance physical function, assistive devices and technology to improve independence, and psychological support and counseling to address emotional well-being. These strategies work together to promote recovery, maximize function, and enhance the overall quality of life for individuals with spinal cord injuries.
Credit: www.nature.com
Frequently Asked Questions For Treat Spinal Cord Injury
What Is The Best Treatment For Spinal Cord Injury?
The best treatment for spinal cord injury is surgery, which can help remove fragments of bones, herniated disks, and stabilize the spine. Additionally, physical therapy and the use of assistive devices can aid in muscle strengthening and mobility.
Is Spinal Cord Damage Repairable?
Spinal cord damage is not currently repairable, but treatments focus on preventing further injuries.
What Are The 5 Signs Of A Spinal Injury?
Here are the 5 signs of a spinal injury:1. Extreme back pain or pressure in the neck, head, or back. 2. Weakness, incoordination, or paralysis in any part of the body. 3. Numbness, tingling, or loss of sensation in the hands, fingers, feet, or toes.
4. Loss of bladder or bowel control. 5. Difficulty with balance and walking.
Q: What Is The Best Treatment For Spinal Cord Injury?
A: The best treatment for spinal cord injury often involves surgery to remove fragments of bones or stabilize the spine to prevent future pain or deformity. Surgery may also be necessary to address herniated disks or fractured vertebrae that are compressing the spine.
Conclusion
Treating spinal cord injury requires a multi-faceted approach that includes surgery, medication, physical therapy, and assistive devices. Surgery may be necessary to remove fragments of bones or stabilize the spine. Medications such as Methylprednisolone can be used to reduce inflammation and promote healing.
Physical therapy helps to strengthen muscles and improve mobility, while assistive devices like wheelchairs and walkers aid in daily activities. Occupational therapy focuses on fine motor skills and communication. It is important to seek immediate treatment after a spinal cord injury to minimize long-term effects.
Although current treatments cannot reverse the damage to the spinal cord, they are aimed at preventing further injuries. Research is ongoing in the field of spinal cord injury treatment, and new approaches are being developed to help patients regain mobility.
Through a combination of medical interventions and rehabilitation therapies, individuals with spinal cord injuries can work towards improving their quality of life.
